Digital Twins and Generative AI in Agriculture
The Rise of Digital Twins and Generative AI in Agriculture
Agriculture is experiencing a technological revolution. One of the most transformative innovations reshaping the industry is the use of digital twins and generative artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies, previously limited to industries like aerospace and automotive, are now paving the way for smarter, data-driven farming. By offering predictive insights and real-time simulation, digital twins and generative AI in agriculture enhance resource management, boost productivity, and support climate resilience.
This blog explores how these technologies work, their applications, and how they are building the foundation for Agriculture 5.0.
What Are Digital Twins in Agriculture?
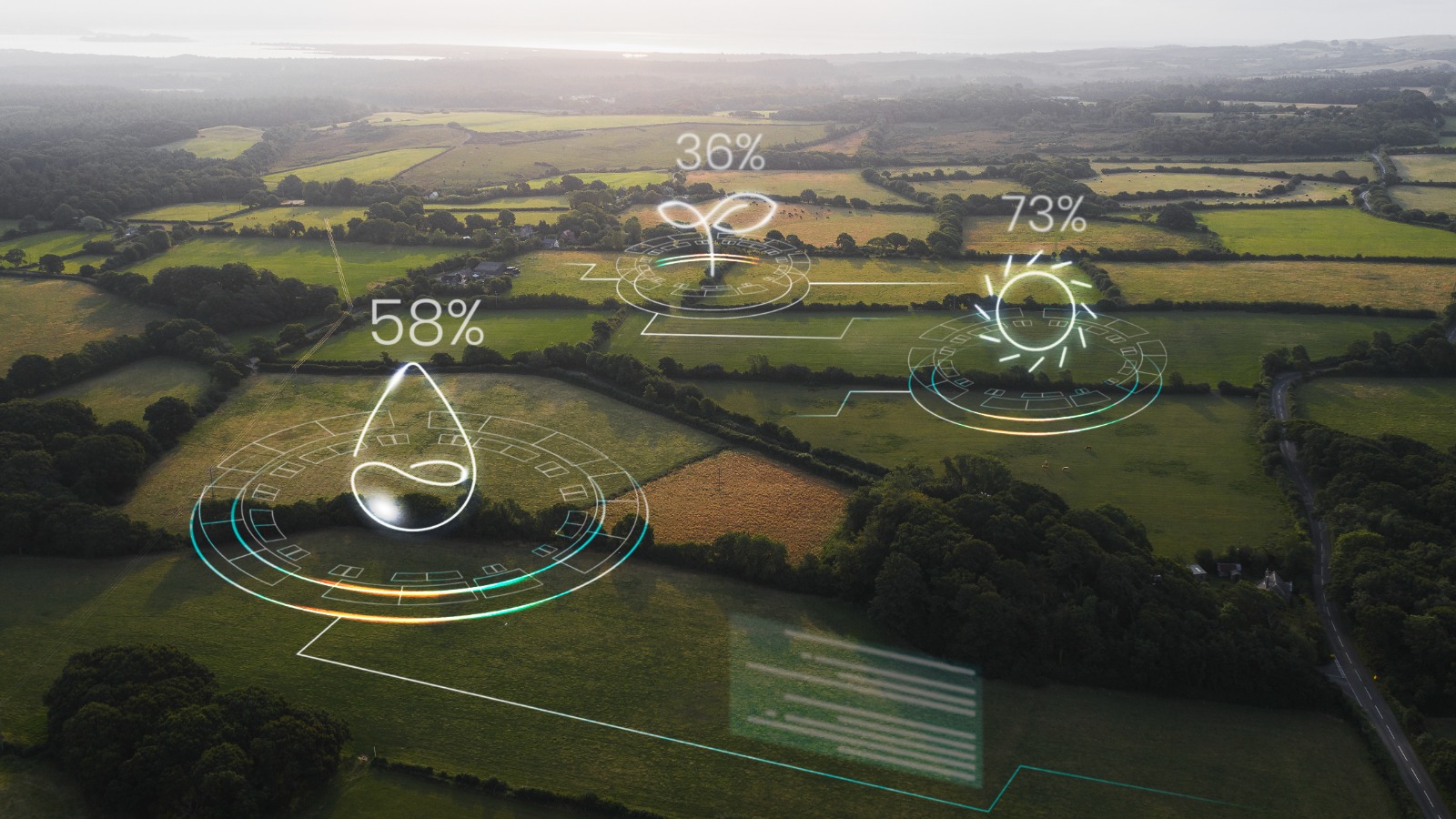
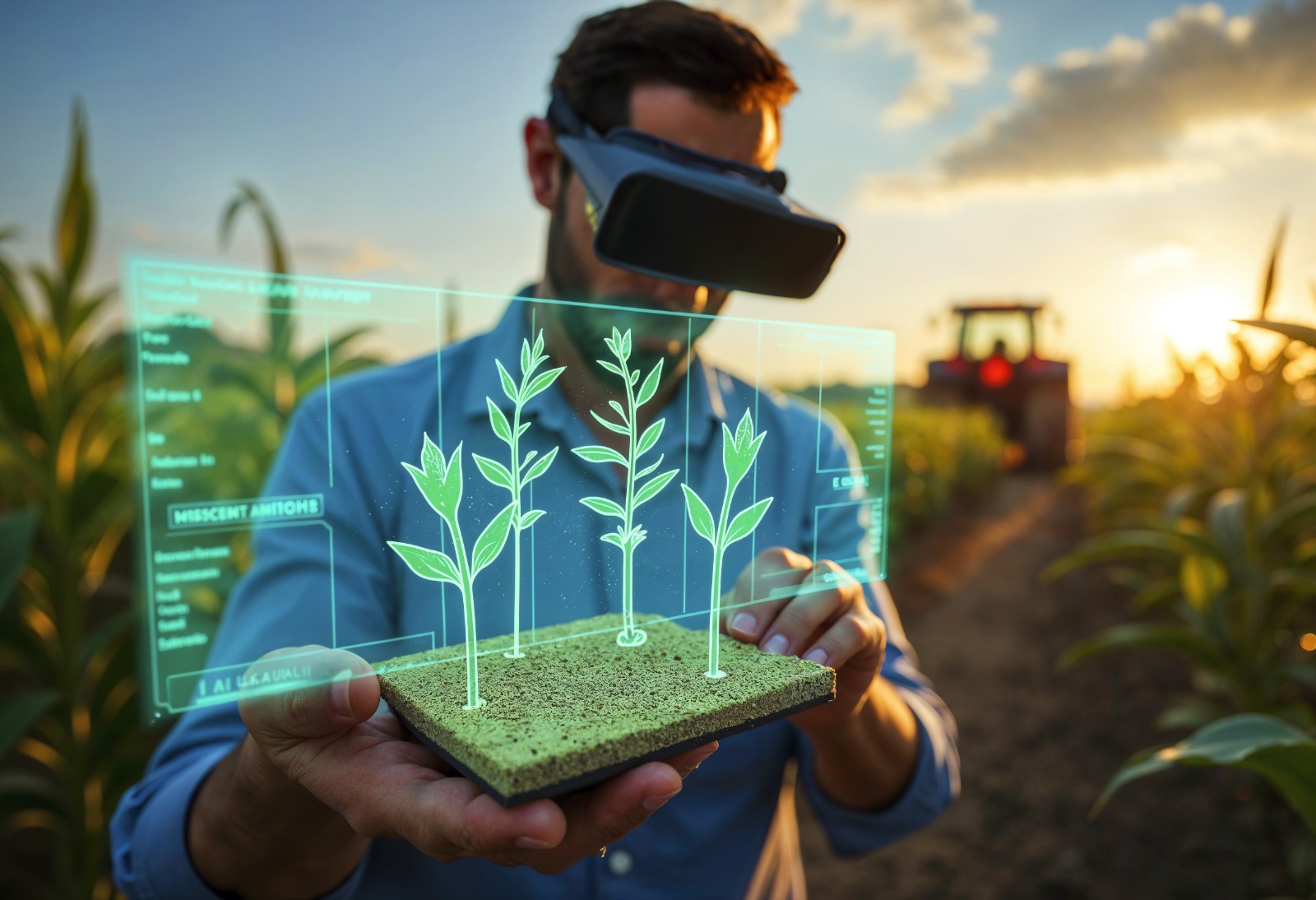
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems, such as crop fields, irrigation systems, or livestock environments. These twins are created using data from sensors, drones, weather stations, and satellites. Once in place, they provide a dynamic model that reflects the real-time condition of the physical environment.
In the context of digital twins in agriculture, these models are used to simulate farming operations, predict outcomes, and optimize resource use. Farmers can test different strategies—such as irrigation levels or fertilizer types—before applying them in real life.
What is Generative AI in Agriculture?
Generative AI refers to a branch of artificial intelligence that can create new data, scenarios, or solutions based on existing information. When applied to farming, generative AI can:
- Predict crop yields based on historical weather data.
- Generate custom fertilizer plans.
- Create simulation models for different climate conditions.
This use of generative AI in agriculture supports innovation and tailored farm management solutions.

Combining Forces: Digital Twins and Generative AI in Agriculture
The real magic happens when digital twins and generative AI are integrated. Together, they create a closed-loop system where data is continuously gathered, analyzed, and used to simulate outcomes and suggest improvements. Here are a few examples:
- Simulate the impact of planting different crop varieties.
- Adjust fertilizer levels based on soil data and predicted weather.
- Model livestock health trends and suggest feeding routines.
Learn more about generative AI in farming
Key Applications of Digital Twins and Generative AI in Agriculture
Precision Agriculture
Digital twins help visualize field conditions, while generative AI recommends customized treatments. Together, they guide precision application of inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides, reducing waste and increasing yield.
Climate Change Adaptation
By simulating climate conditions, generative AI helps farmers select drought-resistant crops. Digital twins provide a view of how these crops might perform under future scenarios.
Livestock Monitoring
With digital twins of barns and livestock pens, farmers can track feed efficiency, animal health, and behavior. Generative AI models suggest dietary adjustments to improve output and welfare.
Greenhouse Optimization
In controlled environments, digital twins monitor light, temperature, and humidity. Generative AI modifies these settings in real-time to enhance plant health.
Supply Chain Management
From farm to market, digital twins help optimize logistics, while generative AI suggests ideal delivery routes and packaging methods.
Benefits of Digital Twins and Generative AI in Agriculture
- Better Decision Making: Access to real-time data and predictive models.
- Higher Efficiency: Lower input costs and improved operational timing.
- Environmental Sustainability: Minimized resource use, lower emissions.
- Yield Optimization: Personalized strategies improve crop and livestock productivity.
- Risk Reduction: Early detection of threats and potential failures.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Twins and Generative AI
- High Initial Investment: Infrastructure and technology can be costly.
- Data Integration: Multiple data sources need harmonization.
- Connectivity Issues: Rural areas often lack robust internet infrastructure.
- Knowledge Gap: Farmers require training to fully use these systems.
Real-World Use Cases
Azure Data Manager for Agriculture (ADMA)
Digital twins are used to simulate planting strategies and analyze real-time soil and weather data.
View project details
John Deere Operations Center
Uses digital twins to model equipment performance. Generative AI suggests maintenance schedules and route planning for field operations.
Corteva Agriscience
Applies generative AI for planting scheme design and stress modeling. This helps farmers select seed hybrids best suited to their environment.
The Future of Farming with Digital Twins and Generative AI
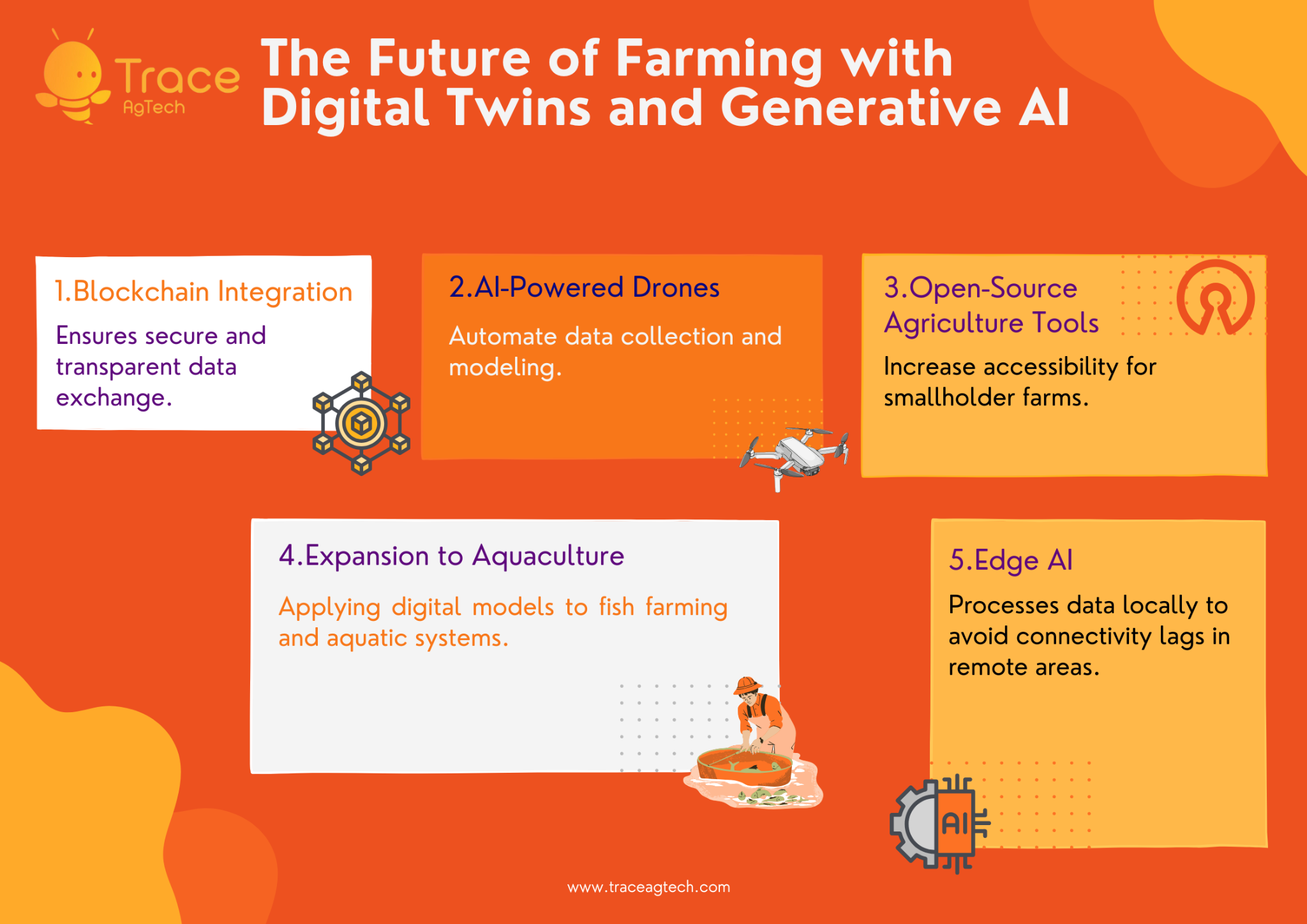
The future holds exciting developments for digital twins and generative AI in agriculture. Some upcoming trends include:
- Blockchain Integration: Ensures secure and transparent data exchange.
- AI-Powered Drones: Automate data collection and modeling.
- Open-Source Agriculture Tools: Increase accessibility for smallholder farms.
- Expansion to Aquaculture: Applying digital models to fish farming and aquatic systems.
- Edge AI: Processes data locally to avoid connectivity lags in remote areas.
Conclusion: A New Era of Smart Agriculture
Digital twins and generative AI in agriculture offer a unique blend of simulation and intelligence that can reshape how food is produced. From small greenhouses to vast fields, these tools empower farmers to make informed, sustainable, and profitable decisions.
As the agriculture sector embraces this digital evolution, the fusion of these technologies could be the key to feeding a growing population in the face of climate change. The journey may be complex, but the harvest will be revolutionary.


Any comments?