Community Supported Agriculture (CSA): A Sustainable Solution
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) is a model of farming where consumers directly support local farmers. This is done by purchasing shares of a farm’s harvest in advance. This arrangement benefits both farmers and consumers. Fostering a closer relationship between the food producer and the consumer while supporting sustainable farming practices and local economies. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of CSA, its benefits, and its impact on local food systems.
What is Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)?
CSA is a farming model that originated in Japan in the 1960s. It was introduced to the United States in the 1980s. It is based on a simple premise: consumers purchase a share of a farm’s harvest at the beginning of the season. In return, they receive a weekly or bi-weekly supply of fresh produce throughout the season. This arrangement allows farmers to receive financial support upfront. Which helps cover the cost of seeds, equipment and labor. While consumers enjoy a steady supply of fresh, locally grown produce.

How Does Community Supported Agriculture Work?
The CSA model typically operates on a subscription basis, where consumers sign up for a share of the harvest before the growing season begins. The cost of a share can vary depending on the size of the share and the length of the season. Some CSAs offer half or full shares, while others may offer different sizes to accommodate varying household sizes.
Once the season begins, members of the CSA receive a box of fresh produce either delivered to their doorstep or available for pickup at a designated location. The contents of the box vary depending on the season and what is currently being harvested on the farm. In addition to fruits and vegetables, some CSAs also offer other products such as eggs, dairy, meat, and baked goods from local producers.
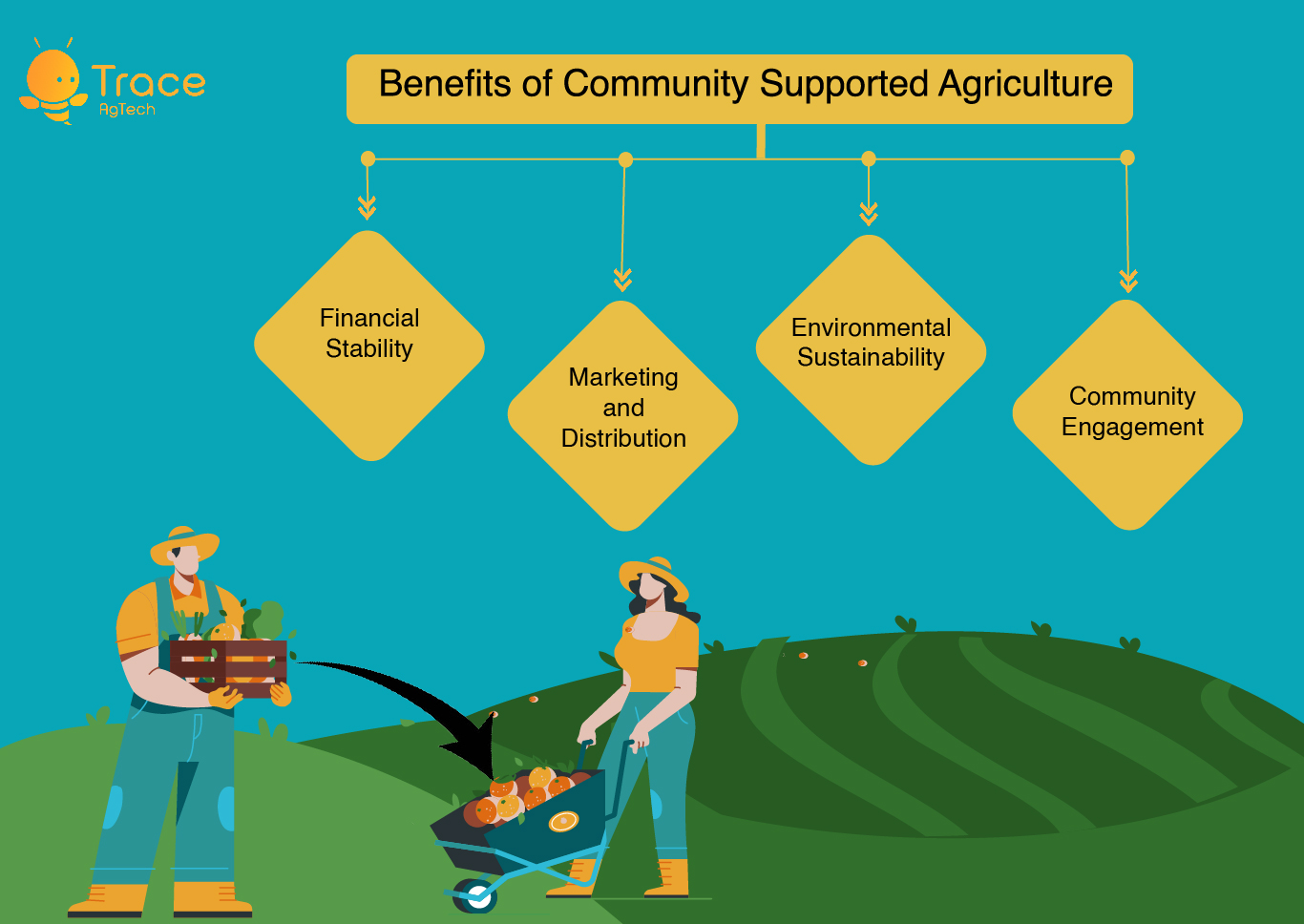
Benefits of Community Supported Agriculture
For Farmers:
- Financial Stability: By selling shares of their harvest upfront, farmers can better predict their income for the season and reduce the risk of financial loss due to crop failure or market fluctuations.
- Marketing and Distribution: CSA provides farmers with a direct marketing channel to consumers, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as wholesalers or retailers. This allows farmers to receive a fair price for their produce and build a loyal customer base.
- Environmental Sustainability: CSA encourages sustainable farming practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced pesticide and fertilizer use, which helps preserve soil health and reduce environmental impact.
- Community Engagement: CSA fosters a sense of community between farmers and consumers, allowing consumers to connect with the people who grow their food and learn more about where their food comes from.
For Consumers:
- Fresh, Nutritious Produce: CSA members enjoy access to fresh, locally grown produce that is often harvested just hours before it is delivered, ensuring maximum freshness and nutritional value.
- Seasonal Variety: CSA introduces consumers to a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, including heirloom and lesser-known varieties that are not commonly found in supermarkets.
- Support Local Economy: By purchasing directly from local farmers, CSA members support their local economy and help create jobs in their community.
- Environmental Impact: CSA reduces the carbon footprint of food production by minimizing the distance that food travels from farm to table, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and refrigeration.
Challenges and Considerations of Community Supported Agriculture
While CSA offers many benefits, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Financial Commitment: Joining a CSA requires a financial commitment upfront. This may be a barrier for some consumers, especially those with limited budgets.
- Seasonal Variability: The contents of a CSA box can vary depending on the season and weather conditions. This may result in some weeks having more limited or repetitive offerings.
- Food Waste: Since CSA boxes often contain a variety of fruits and vegetables. Some members may struggle to consume everything in their box. Leading to potential food waste.
- Limited Control: CSA members have limited control over the contents of their box. This is determined by what is currently being harvested on the farm.
Conclusion
Community Supported Agriculture is a sustainable farming model that benefits both farmers and consumers. It provides financial stability for farmers, access to fresh, locally grown produce for consumers and fostering a closer connection between the two. By supporting local farmers and promoting sustainable farming practices, CSA plays a crucial role in building resilient local food systems and promoting environmental sustainability.


Any comments?