Agriculture Softwares Revolutionized : The Role of Software in Modern Farming
Introduction
Agriculture softwares has helped the industry come a long way from its traditional roots. The modern farmer’s toolkit includes more than just plows and tractors; it now boasts sophisticated software solutions that are transforming the industry. The integration of agriculture software into farming practices has revolutionized the way farmers manage their operations, optimize resources, increase yields, and reduce environmental impacts. In this 1000-word blog post, we’ll explore the pivotal role of agriculture software in shaping the future of farming.
The Evolution of Agriculture Softwares
Historically, farming relied on manual labor and guesswork. Farmers had to rely on their experience and intuition to make decisions about planting, irrigation, and pest control. However, with the advent of computers and the internet, agriculture entered the digital age. Agriculture softwares have been evolving steadily, offering farmers powerful tools to make data-driven decisions and manage their farms more efficiently.
Key Functions of Agriculture Softwares:
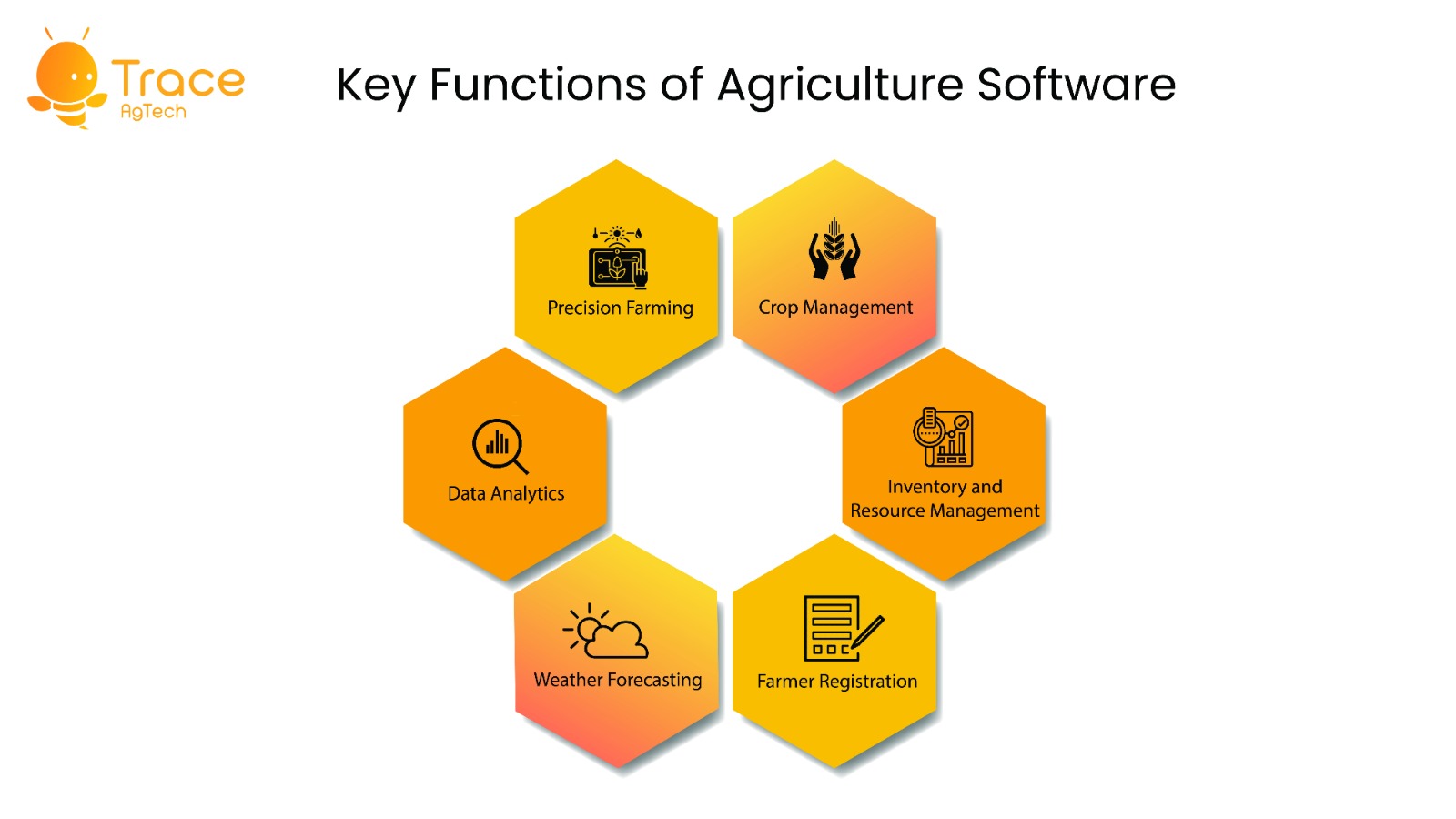
- Precision Farming: One of the most significant advancements in agriculture softwares is precision farming. This technology involves the use of GPS, sensors, and data analytics to optimize various aspects of farming, such as planting, fertilizing, and harvesting. Farmers can create precise planting maps, monitor soil conditions in real-time, and adjust irrigation systems accordingly. This precision leads to higher yields and reduced resource wastage.
- Crop Management: Agriculture softwares offers comprehensive crop management solutions. Farmers can track crop growth, monitor disease and pest outbreaks, and make informed decisions about the application of pesticides and herbicides. This reduces the need for excessive chemical use, benefiting both the environment and the bottom line.
- Inventory and Resource Management: Efficient resource management is crucial for profitability in farming. Agriculture softwares help farmers keep track of their inventory, including seeds, fertilizers, and equipment. By monitoring resource usage, farmers can minimize waste, optimize purchasing decisions, and ensure that they have the necessary inputs at the right time.
- Farmer Registration: With the software comes ease of registering farmer from the field, along with uploading bulk excel for convenience. Agriculture softwares provide tools for on the spot farmer registration, helping farmers decide when to sell their products for maximum profit. This data-driven approach reduces the risk of selling at unfavorable prices.
- Weather Forecasting: Weather plays a crucial role in farming, and agriculture softwares provide access to accurate weather forecasts. Farmers can plan their activities around weather patterns, reducing the risk of crop loss due to adverse conditions.
- Data Analytics: Agriculture softwares collect vast amounts of data from various sources, including sensors, drones, and satellites. Advanced analytics tools help farmers make sense of this data, identifying trends and patterns that can inform decision-making. For example, historical data can be used to predict optimal planting times based on climate conditions.
Benefits of Agriculture Softwares
The adoption of agriculture software offers numerous benefits to farmers and the agriculture industry as a whole:
- Increased Productivity: With precise data and automation, farmers can achieve higher productivity. Precision farming techniques, such as variable-rate seeding and fertilizing, lead to more efficient resource use and greater crop yields.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing resource usage and reducing waste, the software helps farmers cut costs. This includes savings on inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides, as well as labor costs through automation.
- Environmental Sustainability: Agriculture softwares promote sustainable farming practices. Reduced chemical usage, improved irrigation management, and responsible land use all contribute to a more environmentally friendly agriculture industry.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Farmers can make informed decisions based on data rather than intuition. This leads to better outcomes in terms of crop yield, resource management, and profitability.
- Risk Mitigation: Weather forecasting and market analysis tools help farmers mitigate risks associated with unpredictable weather patterns and fluctuating commodity prices.
- Scalability: Agriculture software is adaptable to farms of all sizes, from small family-owned operations to large commercial enterprises. This scalability ensures that all farmers can benefit from these technological advancements.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite its many advantages, the adoption of agriculture software is not without challenges. Some farmers may face barriers such as the initial cost of implementing technology, the need for training, and concerns about data privacy. Additionally, not all regions have equal access to reliable internet connectivity, which can limit the effectiveness of some software solutions.
Looking ahead, the agriculture software industry is poised for further growth and innovation. Here are some trends to watch for in the near future:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML algorithms will become more sophisticated, enabling software to provide even more accurate predictions and recommendations.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance traceability and transparency in the supply chain, helping consumers make more informed choices about the source of their food.
- Integration with IoT Devices: The Internet of Things (IoT) will continue to play a vital role in agriculture, with more devices and sensors being connected to provide real-time data.
- Digital Twins: Digital twin technology will enable farmers to create virtual replicas of their farms, allowing for simulation and testing of different scenarios before implementation.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics will play a larger role in tasks such as planting, harvesting, and even weed control, reducing the need for manual labor.
Conclusion
Agriculture softwares has revolutionized farming by offering powerful tools for precision, efficiency, and sustainability. From precision farming to market analysis, these software solutions empower farmers to make data-driven decisions that lead to increased productivity and profitability. As technology continues to advance, agriculture software will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of farming, ensuring that we can meet the world’s growing demand for food while minimizing environmental impacts. Farmers who embrace these tools will be well-positioned to thrive in the ever-evolving landscape of modern agriculture.


Any comments?