Cultivating a Sustainable Future: Unveiling the Promise of Climate-Smart Agriculture
Climate change poses an unprecedented threat to global food security. Rising temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and extreme events are impacting agricultural productivity, jeopardizing the livelihoods of millions. In response to these challenges, the concept of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) has emerged as a beacon of hope. CSA seeks to transform traditional farming practices into a resilient, sustainable, and adaptive system that not only mitigates climate change but also ensures food security. In this blog, we will explore the key principles of Climate-Smart Agriculture, its benefits, challenges, and the role it plays in shaping a more sustainable and resilient agricultural future.
Understanding Climate-Smart Agriculture:
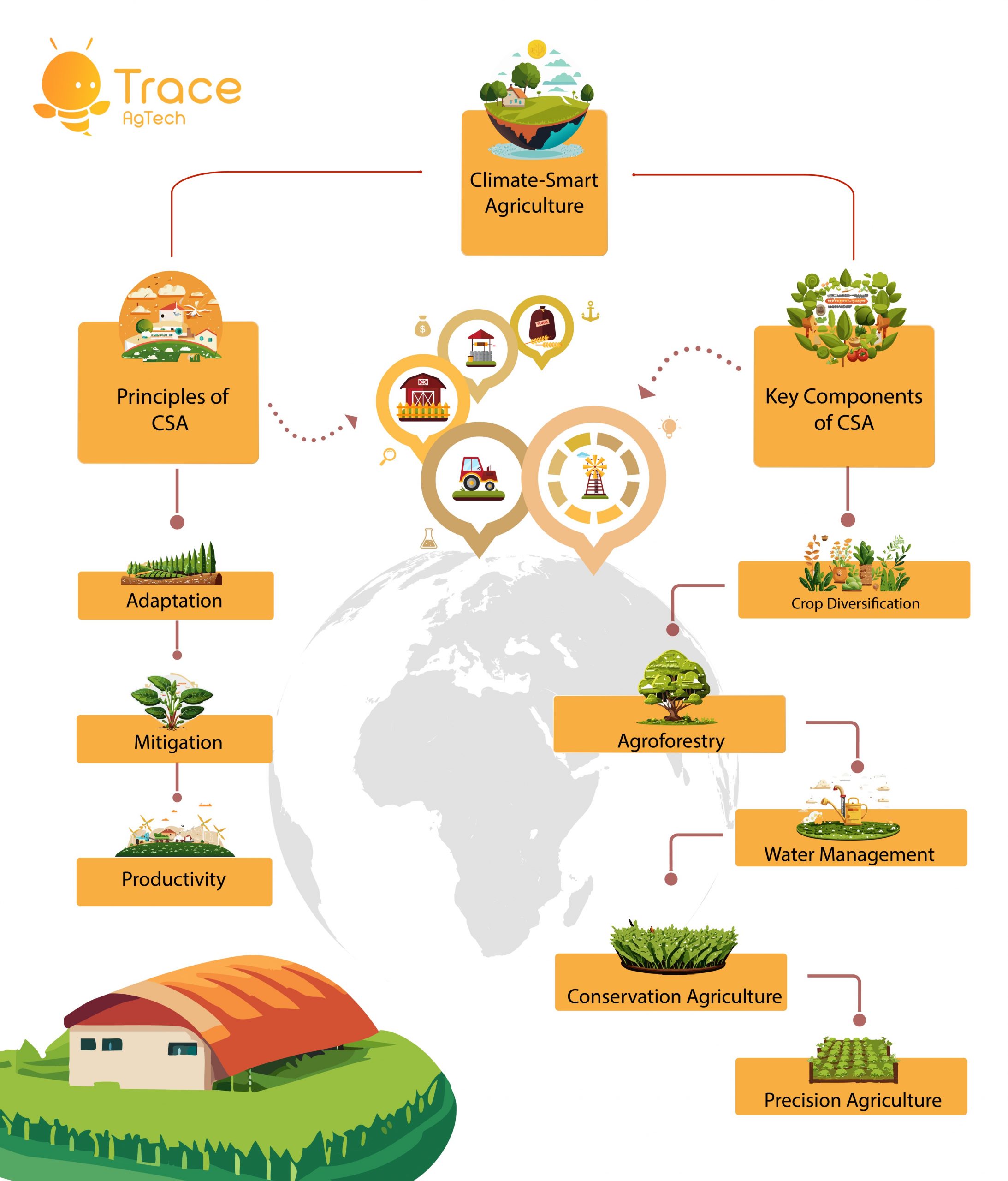
- Definition and Principles of CSA: Climate-Smart Agriculture is an approach that integrates three main pillars: climate change adaptation, mitigation, and increased productivity. It aims to enhance the resilience of farming systems to climate variability and change while promoting sustainable and efficient resource use. The three key principles of CSA are:a. Adaptation: CSA focuses on building the resilience of agricultural systems to climate impacts, such as changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events.b. Mitigation: CSA seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture by promoting practices that enhance carbon sequestration and decrease the carbon footprint of farming.c. Productivity: CSA aims to increase agricultural productivity sustainably, ensuring food security for a growing global population.
- Key Components of CSA: CSA encompasses a range of practices and technologies tailored to local contexts. Some essential components include:a. Crop Diversification: Planting a variety of crops helps farmers adapt to changing climate conditions and reduces vulnerability to pests and diseases.b. Agroforestry: Integrating trees into farming systems improves biodiversity, enhances water retention, and sequesters carbon, contributing to both adaptation and mitigation.c. Water Management: Efficient water use, through technologies like drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, helps farmers adapt to changing precipitation patterns.d. Conservation Agriculture: Practices such as minimal tillage, cover cropping, and crop rotation promote soil health, reduce erosion, and enhance carbon sequestration.e. Precision Agriculture: Employing technology, such as sensors and satellite imagery, enables farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
Benefits of Climate-Smart Agriculture:
- Enhanced Resilience: CSA practices enhance the resilience of farming systems by diversifying crops, improving water management, and adopting climate-resilient varieties. This resilience helps farmers withstand the impacts of extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and storms.
- Sustainable Resource Use: By promoting sustainable practices like conservation agriculture and agroforestry, CSA optimizes resource use. This leads to increased water and soil conservation, reduced use of agrochemicals, and improved overall environmental sustainability.
- Increased Productivity: Climate-Smart Agriculture aims to boost productivity through the adoption of advanced technologies and sustainable practices. This not only ensures food security but also provides economic benefits for farmers, contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas.
- Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction: Practices like agroforestry and conservation agriculture contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating the impact of agriculture on climate change. Additionally, precision agriculture helps reduce emissions by optimizing fertilizer and pesticide use.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption:
- Lack of Awareness and Knowledge: Many farmers are unaware of the benefits of CSA practices or lack the necessary knowledge to implement them effectively. Providing education and extension services is crucial to overcoming this barrier.
- Financial Constraints: Adoption of CSA practices often requires upfront investments in new technologies and infrastructure. Many smallholder farmers face financial constraints, hindering their ability to invest in climate-smart solutions.
- Policy and Institutional Support: Inconsistent or inadequate policy support can impede the widespread adoption of CSA. Governments and institutions need to create an enabling environment through supportive policies, incentives, and extension services.
- Market Access and Value Chains: Limited market access and poorly developed value chains for climate-smart products can discourage farmers from adopting CSA. Strengthening these aspects is essential to ensuring that farmers benefit economically from sustainable practices.
- Climate Variability and Uncertainty: Climate-smart practices must adapt to the unpredictable nature of climate change. Farmers face challenges in planning and implementing strategies when faced with uncertain weather patterns and shifting climate conditions.
Role of Technology in Climate-Smart Agriculture:
- Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture utilizes technology such as sensors, drones, and satellite imagery to collect data on soil health, weather conditions, and crop performance. This data-driven approach allows farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency.
- Climate Information Services: Providing farmers with timely and accurate climate information is crucial for decision-making. Climate information services, often delivered through mobile apps or community-based networks, help farmers plan their activities based on weather forecasts and climate predictions.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Water scarcity is a significant challenge in agriculture. Smart irrigation systems, including drip and precision irrigation, help farmers optimize water use, reducing both water waste and energy consumption.
- Biotechnology and Climate-Resilient Crops: Biotechnology plays a role in developing climate-resilient crops that can withstand extreme weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Genetic modification techniques can enhance crop yields and reduce vulnerability.
- Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology can improve transparency and traceability in agricultural supply chains. This ensures that products labeled as climate-smart are produced using sustainable practices, providing consumers with confidence in their choices.
Success Stories and Case Studies:
- Kenya: Climate-Smart Villages: In Kenya, the Climate-Smart Villages project, implemented by the CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture, and Food Security (CCAFS), focuses on promoting CSA practices tailored to local conditions. This includes improved water management, agroforestry, and climate-resilient crop varieties. The project has shown positive impacts on food security and farmers’ incomes.
- India: SRI (System of Rice Intensification): The System of Rice Intensification (SRI) is a climate-smart approach to rice cultivation that has gained popularity in India. SRI focuses on improved planting techniques, water management, and organic inputs, resulting in increased yields, reduced water use, and enhanced resilience to climate variability.
- Vietnam: Agroecological Farming Practices: In Vietnam, agroecological farming practices, including intercropping, agroforestry, and organic farming, have been successfully adopted. These practices enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and reduce the reliance on chemical inputs, contributing to climate resilience and sustainability.
Future Outlook and Recommendations:
- Scaling Up CSA Practices: To address the challenges and unlock the full potential of Climate-Smart Agriculture, there is a need to scale up successful practices. This requires concerted efforts from governments, NGOs, and the private sector to provide support, resources, and incentives for farmers to adopt CSA.
- Capacity Building and Education: Investing in farmer education and extension services is crucial for the widespread adoption of CSA. This includes training programs on sustainable practices, the use of technology, and climate-smart approaches tailored to local contexts.
- Financial Support and Incentives: Governments and financial institutions should provide financial support and incentives to farmers for adopting CSA practices. This could include subsidies, low-interest loans, and insurance schemes to mitigate the financial risks associated with transitioning to climate-smart agriculture.
- Research and Innovation: Continued research and innovation are essential to develop new and improved CSA practices. This includes the development of climate-resilient crop varieties, innovative water management techniques, and sustainable pest and disease management strategies.
- Policy Alignment and Collaboration: Governments should align policies to support CSA and foster collaboration between different stakeholders, including farmers, researchers, NGOs, and the private sector. A coordinated approach is necessary to create an enabling environment for the widespread adoption of climate-smart practices.
Conclusion:
Climate Smart Agriculture stands at the forefront of efforts to address the challenges posed by climate change in the agricultural sector. By integrating adaptation, mitigation, and increased productivity, CSA offers a holistic approach to creating a more sustainable and resilient food system. While challenges exist, the successes of various projects and the potential of technology underscore the promise of CSA in securing the future of agriculture. With continued support, innovation, and collaboration, Climate-Smart Agriculture can pave the way for a more sustainable and climate-resilient global food system, ensuring that farmers thrive in the face of a changing climate.


Any comments?