Ensuring Food Security: A Global Imperative
Food security stands as one of the most pressing challenges facing our world today. As the global population continues to surge and the impacts of climate change intensify, ensuring that everyone has access to safe, nutritious, and affordable food has become a critical issue. The concept of food security encompasses not only the availability of food but also its accessibility, utilization, and stability. In this blog, we delve into the complexities of food security, its importance, and the strategies being employed to address this vital global concern.
Understanding Food Security
At its core, food security implies that all individuals, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and preferences for an active and healthy life. The four dimensions of food security are:
- Availability: Sufficient quantities of food are consistently produced or imported to meet the needs of the population.
- Accessibility: Individuals have the means to acquire food through purchase, production, or exchange.
- Utilization: People are able to use the food they acquire to meet their nutritional needs and maintain good health.
- Stability: Access to food is secure over time, even in the face of shocks such as natural disasters or economic disruptions.
Importance of Food Security
Food security is a fundamental human right and a critical foundation for social stability and economic development. Without proper access to nourishing food, individuals’ health deteriorates, leading to malnutrition, stunted growth, and susceptibility to diseases. Children and pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to the long-term consequences of inadequate nutrition.
From a societal perspective, food insecurity can exacerbate social inequalities and contribute to political instability. Regions with insufficient food access often experience migration as people search for better opportunities, straining resources in both origin and destination areas. Moreover, food price volatility can trigger social unrest and disrupt economic growth.
Challenges to Achieving Food Security
Several factors contribute to the complexity of achieving global food security:
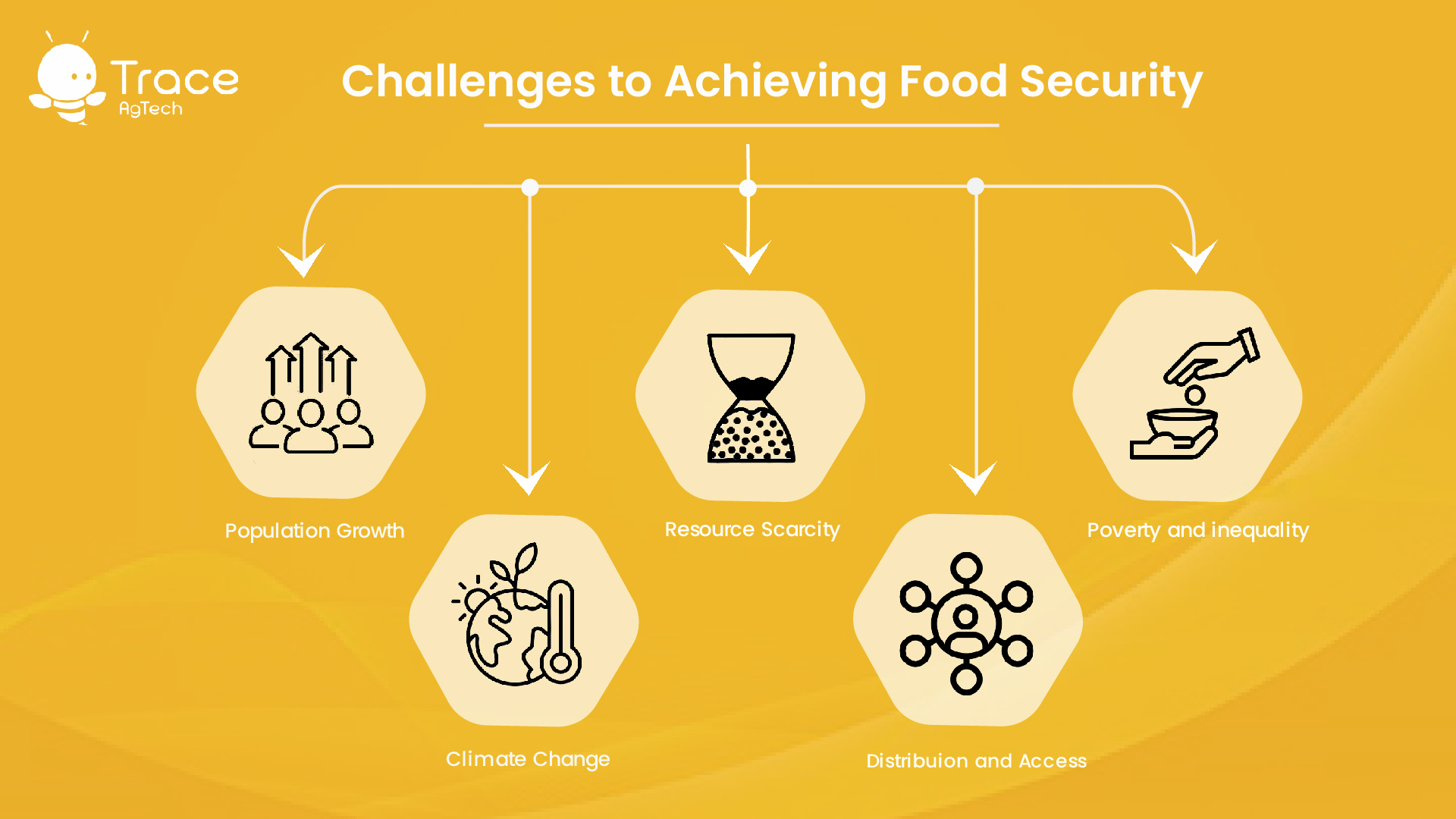
- Population Growth: As the world’s population continues to expand, the demand for food rises proportionally. This necessitates increased agricultural production while preserving environmental resources.
- Climate Change: Erratic weather patterns, rising temperatures, and extreme events challenge agricultural productivity. Droughts, floods, and heatwaves can lead to crop failures and reduced food availability.
- Resource Scarcity: Land degradation, water scarcity, and diminishing arable land limit agricultural expansion. Sustainable land and water management practices are crucial for maintaining food production.
- Distribution and Access: Even when food is available, unequal distribution and inadequate infrastructure can hinder access for marginalized communities.
- Poverty and Inequality: Economic disparities often prevent vulnerable populations from accessing nutritious food. Addressing poverty is integral to achieving food security.
Strategies for Enhancing
Governments, international organizations, NGOs, and communities around the world are actively working to tackle the complexities:
- Sustainable Agriculture: Promoting practices such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and organic farming minimizes soil degradation, preserves biodiversity, and enhances long-term food production.
- Technology and Innovation: Implementing advanced agricultural technologies, such as precision farming, genetically modified crops, and efficient irrigation systems, can boost yields and improve resilience.
- Diversification of Diets: Encouraging a diverse diet can enhance nutrition and reduce dependence on a limited number of staple crops, making communities more resilient to crop failures.
- Empowering Smallholder Farmers: Supporting small-scale farmers with access to credit, markets, and training enables them to increase their productivity and contribute significantly to local food supplies.
- Social Safety Nets: Implementing social programs like food assistance, school feeding, and cash transfer programs helps vulnerable populations access essential nutrition.
- Climate Resilience: Developing climate-smart agriculture that adapts to changing climatic conditions and mitigates their impacts is crucial for maintaining food production in the face of environmental challenges.
- Reducing Food Waste: A significant portion of food produced is lost or wasted, exacerbating food insecurity. Reducing food waste along the supply chain can increase food availability.
- Global Partnerships: Collaborative efforts among governments, organizations, and stakeholders are essential to address food security on a global scale.
Conclusion
Food security is an intricate issue that requires a multifaceted approach. As the world’s population continues to grow and the effects of climate change become more pronounced, ensuring access to nutritious food for all becomes increasingly urgent. By embracing sustainable agricultural practices, technological innovation, poverty alleviation strategies, and international cooperation, we can pave the way for a future where food security is no longer a distant aspiration, but a fundamental reality for every individual on this planet.


Any comments?