Food Waste in Agriculture: Tackling & Addressing the Root Cause
Food waste is a significant global issue, with roughly one-third of all food produced worldwide being lost or wasted annually. In the agricultural sector, food waste occurs at various stages of production, from the farm to the consumer. This blog explores the root causes of food waste in agriculture and discusses potential solutions to mitigate this critical problem.
The Scope of the Issue
Food waste in agriculture encompasses several interrelated challenges. On the farm, factors such as overproduction, imperfect produce standards, and inefficient harvesting techniques contribute to significant losses. Additionally, post-harvest losses occur during processing, storage, and transportation. Finally, consumer behavior, including purchasing habits and food disposal practices, also plays a role in food waste.
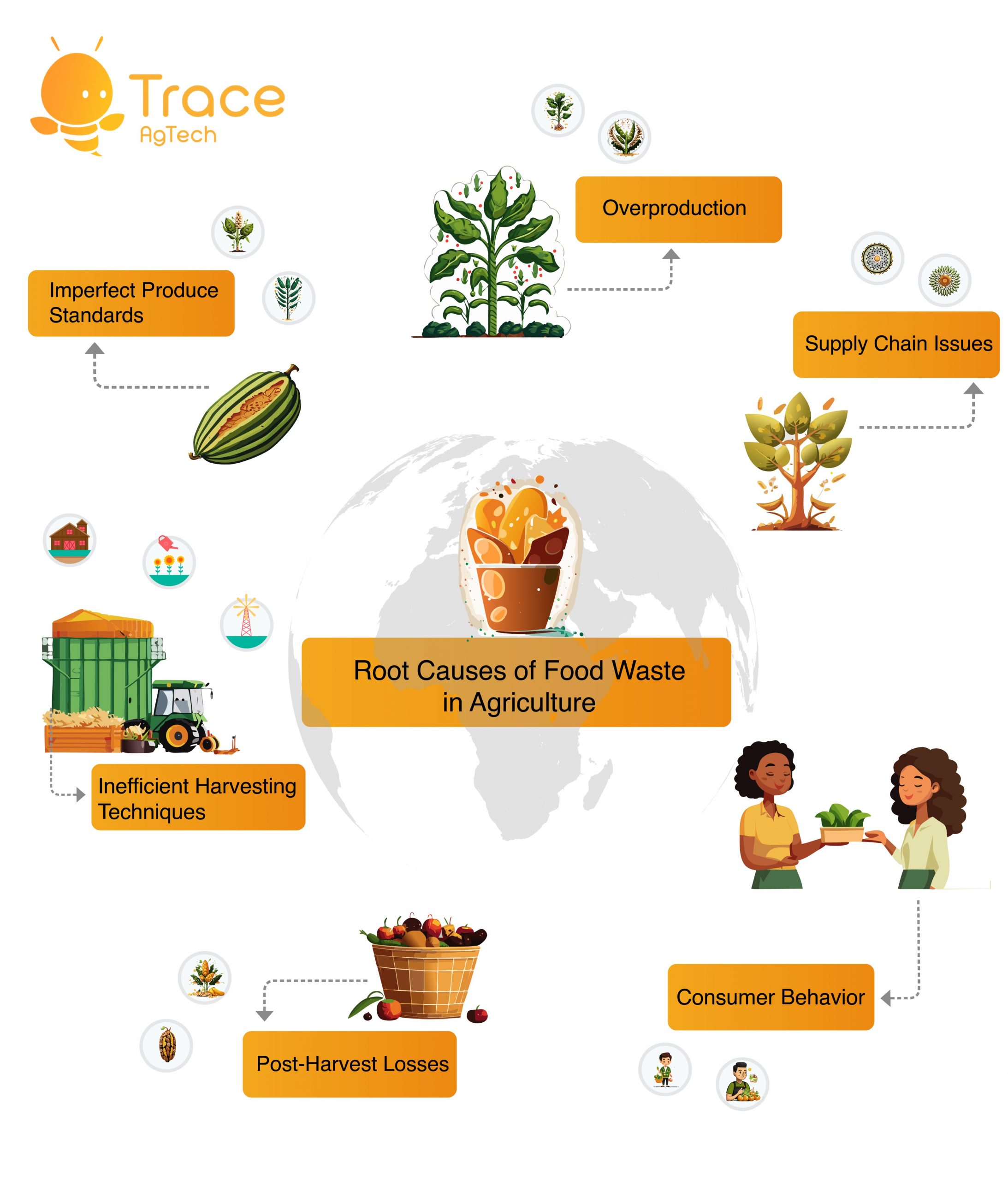
Root Causes of Food Waste in Agriculture
Food waste in agriculture is a complex issue with multiple root causes that contribute to significant losses in the food supply chain. Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective strategies to reduce food waste and create a more sustainable food system. Some of the primary root causes of food waste in agriculture include:
- Overproduction: Farmers often overproduce to ensure they meet market demand and have enough to sell. However, this can lead to surplus produce that goes to waste if not sold or utilized in time. Factors such as unpredictable weather conditions and fluctuating market prices can also contribute to overproduction.
- Imperfect Produce Standards: Strict cosmetic standards set by retailers and consumers result in the rejection of perfectly edible but “imperfect” fruits and vegetables. Produce that does not meet these standards is often left unharvested or discarded, leading to significant waste at the farm level.
- Inefficient Harvesting Techniques: Manual harvesting methods, such as handpicking, can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. These methods can also result in damage to the produce, making it unsuitable for sale or consumption. In some cases, farmers may lack access to appropriate tools and technology that could improve harvesting efficiency and reduce losses.
- Post-Harvest Losses: After harvesting, fruits and vegetables are susceptible to spoilage if not stored properly. Inadequate storage facilities, such as lack of refrigeration or proper ventilation, can lead to spoilage and waste. Poor transportation networks can also contribute to post-harvest losses, as produce may be damaged or spoiled during transit.
- Consumer Behavior: Consumer behavior plays a significant role in waste at the retail and consumer levels. Consumers often purchase more food than they need, leading to excess that is eventually discarded. Additionally, confusion over expiration dates and improper storage practices can contribute to household waste.
- Supply Chain Issues: Food waste can occur at various points in the supply chain, including during processing, packaging, and distribution. Inefficient supply chain management, such as delays in transportation or inadequate inventory management, can lead to losses and waste.
Impacts of Food Waste
Food waste in agriculture has significant economic, social, and environmental impacts. Economically, it represents a loss of resources invested in production, transportation, and distribution. Socially, it contributes to food insecurity and hunger, as resources that could have been used to feed people are wasted. Environmentally, food waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and wastes water, energy, and land resources.
Addressing Food Waste: Solutions and Initiatives
Food waste in agriculture is a complex issue, but several solutions and initiatives can help mitigate this problem. These solutions target various stages of the food supply chain, from production to consumption, and involve stakeholders at different levels. Here are some effective strategies to reduce waste in agriculture:
- Improved Production Practices: Implementing precision agriculture techniques, such as using sensors and data analytics, can help farmers optimize resource use and reduce overproduction. This includes using water more efficiently, applying fertilizers judiciously, and reducing the use of pesticides.
- Rethinking Produce Standards: Encouraging the consumption of “ugly” produce that may not meet strict cosmetic standards can help reduce waste at the farm and retail levels. Educating consumers about the value of imperfect fruits and vegetables can also help change perceptions and reduce waste.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Building and improving storage and transportation infrastructure can help reduce post-harvest losses. This includes investing in cold storage facilities, better packaging materials, and efficient transportation networks. In developing countries, improving infrastructure is crucial for reducing food and improving food security.
- Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency: Improving supply chain management practices, such as better inventory management, transportation planning, and coordination among stakeholders, can help reduce waste at various stages of the supply chain. Technologies like blockchain can also help improve traceability and transparency in the supply chain, reducing the risk of waste.
- Consumer Education: Educating consumers about proper food storage, meal planning, and understanding expiration dates can help reduce household food waste. Providing tips and resources on how to reduce waste at home can also empower consumers to make more sustainable choices.
- Food Recovery and Donation Programs: Establishing food recovery and donation programs can help redirect surplus food to those in need. These programs can work with farmers, retailers, and food manufacturers to rescue edible food that would otherwise be discarded and distribute it to food banks, shelters, and other organizations.
- Policy and Regulation: Governments can play a crucial role in reducing food waste by implementing policies and regulations that incentivize waste reduction. This can include tax incentives for donations, regulations on date labeling, and support for waste reduction initiatives.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration among stakeholders, including farmers, producers, retailers, policymakers, and consumers, is essential for addressing food waste. Partnerships between different sectors can help develop innovative solutions and create a more sustainable food system.
By implementing these solutions and initiatives, we can work towards reducing waste in agriculture and creating a more sustainable food system for future generations.
Conclusion
Food waste in agriculture is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. Addressing this problem requires a multi-faceted approach that involves stakeholders at all levels of the food supply chain. By implementing sustainable production practices, rethinking consumer behavior, and investing in infrastructure, we can work towards reducing food waste and building a more sustainable food system for future generations.


Any comments?