GHG Data Monitoring in AgTech
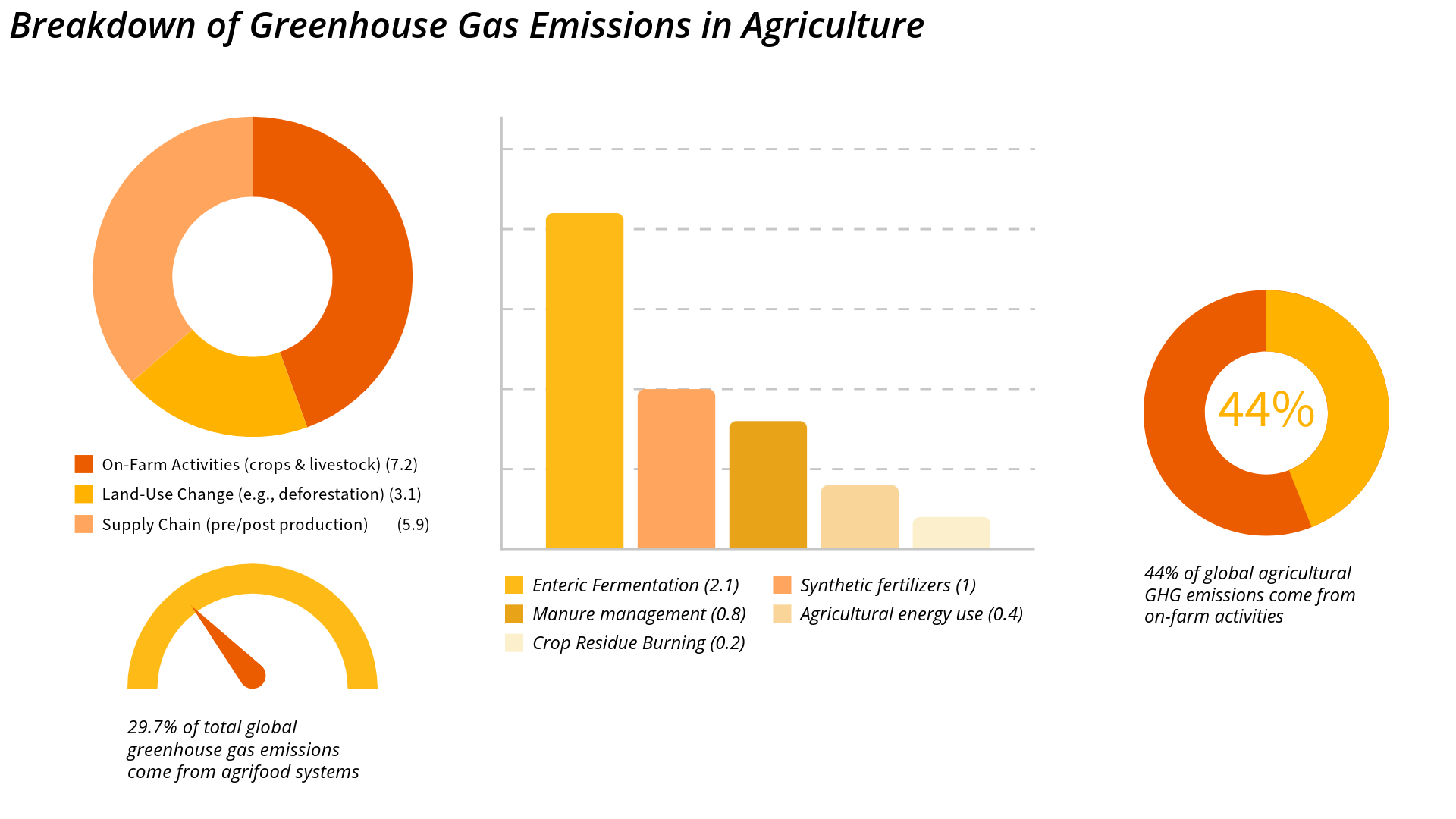
Agriculture is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions— and as the world pushes toward climate goals, the sector is under increasing pressure to measure and reduce its environmental impact. That’s where GHG data monitoring comes in. For AgTech companies, it’s not just about compliance anymore; it’s about building smarter, more sustainable systems that are future-ready.
What is GHG Monitoring in Agriculture?
GHG data monitoring is the process of tracking emissions across the agricultural value chain — from pre-planting to post-harvest. This includes:
- CO₂ from fuel and energy use
- CH₄ from livestock and waste
- N₂O from nitrogen fertilizers
These gases contribute significantly to climate change, and understanding where, when, and how they are produced is the first step toward reducing them.
On-Farm Emissions Monitoring
On the farm, emissions come from everyday activities — and tracking them in real time helps uncover both inefficiencies and opportunities for sustainability. GHG data monitoring in AgTech enables better decision-making for emission reduction.
Key sources include:
-
Fertilizer application (especially nitrogen-based)
-
Diesel or fuel-powered equipment
-
Soil management and tillage practices
AgTech tools used:
-
IoT sensors and smart field devices
-
Satellite and drone-based imagery
-
Farm management platforms for input tracking
These tools not only help measure emissions but also guide better decision-making for resource efficiency.
Post-Harvest Emissions
Post-harvest operations are often overlooked in GHG reporting — yet they can contribute significantly to a farm’s carbon footprint.
Tracked areas include:
-
Storage facilities (especially cold storage)
-
Processing centers and packaging
-
Transportation logistics
By extending GHG data monitoring beyond the farm, AgTech companies can provide full-chain transparency and support decarbonization at every stage.
Complete Carbon Accounting
True sustainability isn’t just about emissions — it’s also about recognizing climate-positive practices.
AgTech platforms must capture:
-
Both emissions and offsets
-
Carbon-negative activities like:
-
Cover cropping
-
Reduced tillage
- Biochar application
-
This data is critical for ESG reporting, carbon offset programs, and certification standards.
Why GHG Monitoring Matters?
Implementing GHG data monitoring in AgTech brings multiple benefits, including:
-
Improved operational efficiency
-
Data for sustainability certifications and audits
-
Access to climate-conscious markets and investors
-
Compliance with evolving regulations
-
Stronger trust with consumers and partners
It’s a foundational step toward building Net Zero agricultural systems.
Conclusion
As sustainability standards tighten and climate accountability becomes non-negotiable, GHG data monitoring is no longer optional — it’s essential. For AgTech companies, tracking emissions across the entire value chain unlocks operational insights, regulatory readiness, and competitive advantage.
By leveraging accurate, real-time emissions data, businesses can lead the transition to a low-carbon agricultural future — and support their partners in doing the same.


Any comments?